From all of us at Business Extension Bureau, have a safe and happy new year!
Author Archives: bebtexas
Happy New Year
Happy Holidays!
Happy Holidays from all of us at BEB-Business Extension Bureau!
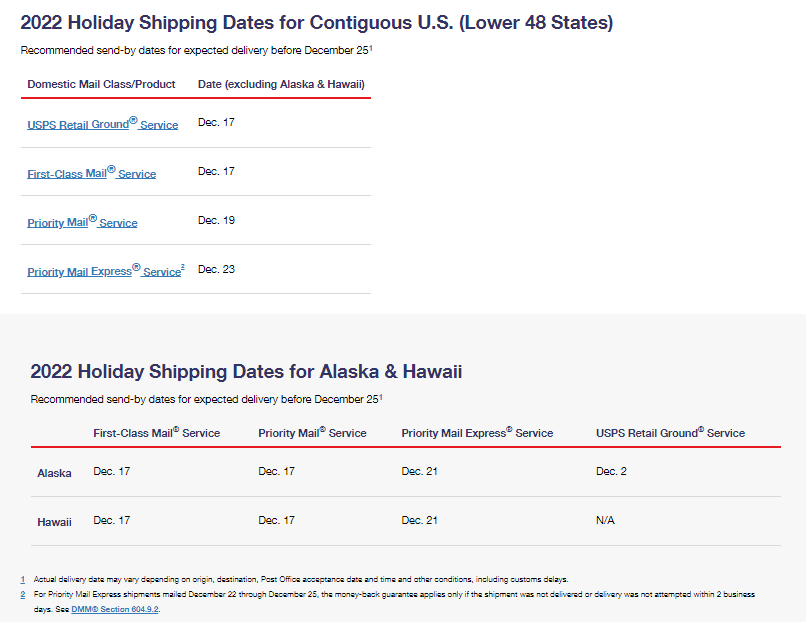
Holiday 2020 Mail Dates-Domestic
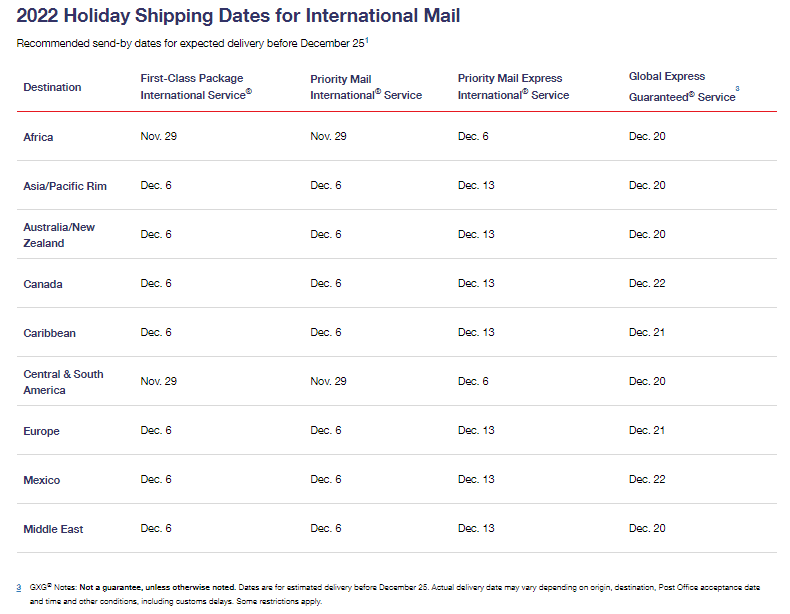
Holiday 2022 Mail Dates-International
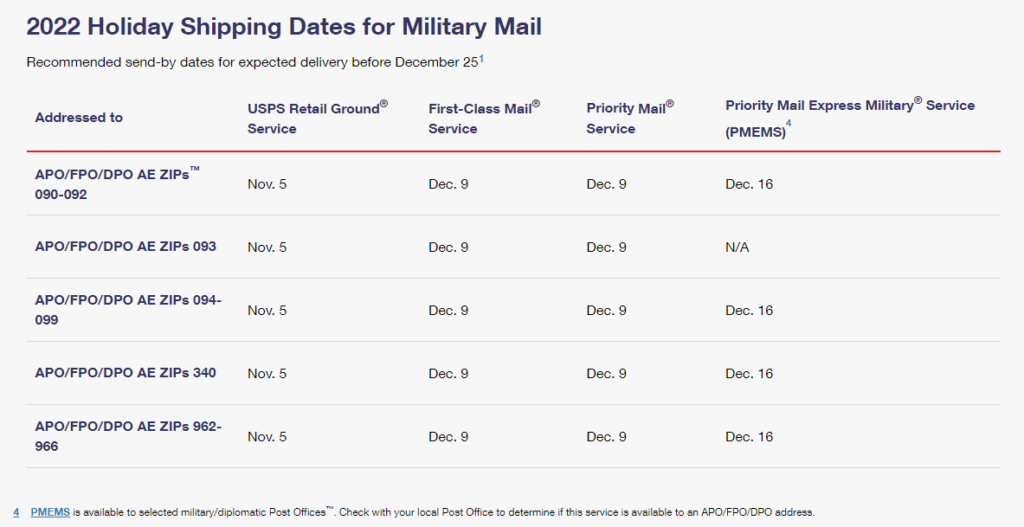
Holiday 2022 Mail Dates-Military Mail

 For more information click here.
For more information click here.
Create Your Marketing Strategy in 4 Easy Steps – Did it Work?
The holidays are over, and things are quieting down a little. It is time for you review your efforts and determine if it worked. We suggest that you block out 3-5 hours for just one day so you can really see the results. Study and do the math.
- Was the time and money spent worth the results?
- Did your sales exceed your original plan?
- Study your website traffic compared to sales and when your marketing steps were executed.
For example, we find that after a direct mail campaign has delivered, almost 100% of the time, website traffic for that business increases by double digits. Study to see if your store sales also increased during those accelerated periods.
Review sales compared to your social paid advertisements and your organic posts. Taking the uninterrupted time to research and study your results will guide you through your next quarterly marketing strategy. You will know exactly where you need to reduce and/or increase your marketing dollars and time.
Create Your Marketing Strategy in 4 Easy Steps – Schedule It
Now it’s time to schedule the implementation of your strategy. This allows you to maintain consistency with your audiences and it is vital to the success of your plan. This is where you can delegate and integrate your staff, agency, printer/mailer, or family and friends.
 Keep your schedule in a place where everyone involved can see it and try to stay on schedule.
Keep your schedule in a place where everyone involved can see it and try to stay on schedule.
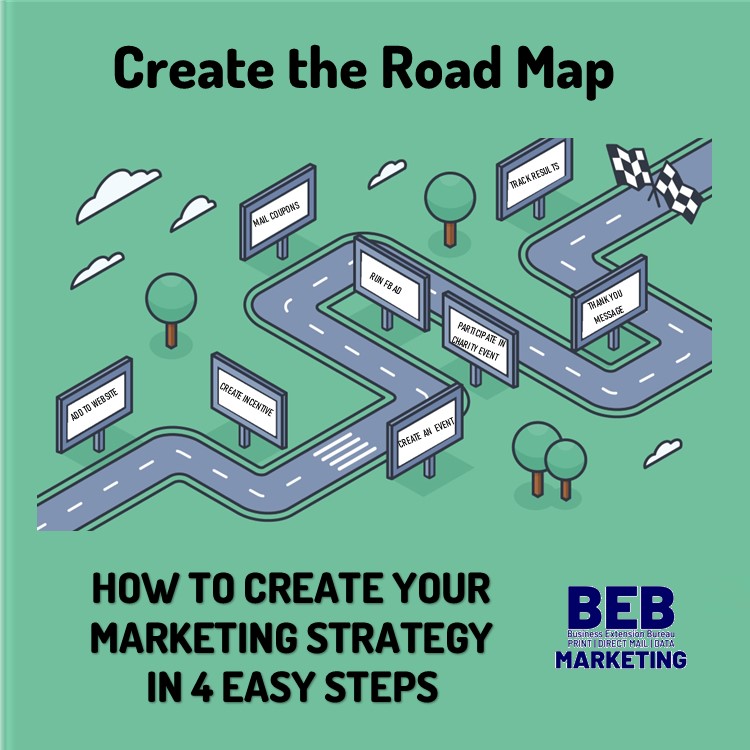
Creating Your Marketing Strategy Plan
Map Out The Basics
Last week determined our goal. We wanted to increase online gift certificate sales by 5% compared to last 4th quarter. Now it’s time to map the strategy, meaning how are we going to do it?
We need to get the word out that we have gift certificates available, we need to ask ourselves; How?
- Set your timeframe: October 1 through December 31
- Add an image to the website home page carousel
- Set/up the ability to buy gift certificates online
- Create an incentive (get 5% off your next purchase when you buy a $100 Gift Certificate)
- Create an event/sale to draw new customers into the store
- Get involved in a toy drive for a local charity
- Budget and create social media ads
- Budget and create a direct mail marketing campaign
- Create special Thank You messages
- Determine how to track our progress
Before you know it, you’ll have your 4th quarter marketing strategy completed and ready to implement!
Create Your Marketing Strategy in 4 Easy Steps
A strategy of any kind involves four things:
- Define Your Mission
- Create A Plan
- Create Steps To Implement The Plan
- Once Executed, Determine If It Worked
Many people get ‘stuck’ when creating a marketing strategy because they often confuse tactics with strategy. Unlike a strategy, a tactic is a step within a plan. A strategy, however, is the plan.
Define Your Mission-Establish Your Goals
Set specific, clearly defined goals. Not, “I want to sell more merchandise this year”. Making goals that are obscure or unrealistic is the equivalent to not making any goals at all, and will be impossible to track or to achieve.
Instead, set specific goals that are reasonable. A good example is I want to increase gift certificate sales by 5% over last fourth quarter. A specific goal like this allows you to track progress and determine what is working and what isn’t.
Join us next week for how to create “The Plan”.





 Click here for more details
Click here for more details